Categories
Tags
2263 words
11 minutes
2024 网鼎杯
crypto1
题面:
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from secret import flag
p = getPrime(512)
q = getPrime(512)
n = p * q
d = getPrime(299)
e = inverse(d,(p-1)*(q-1))
m = bytes_to_long(flag)
c = pow(m,e,n)
hint1 = p >> (512-70)
hint2 = q >> (512-70)
print(f"n = {n}")
print(f"e = {e}")
print(f"c = {c}")
print(f"hint1 = {hint1}")
print(f"hint2 = {hint2}")
n = 102986063343828181691017061322961752231482650979117614592328540336319559999419987417702811972323418742113520151888629472567603955481992514927285801019993715247868027388036294100323295206260750653997980051233409135844852567338000284382992259587294344858347675971990058869658603742150067210112531948312675289517
e = 94332227188033251470419190704216678578924281824166571884737945076375866824249376355159909654478713223003101525619990336866998705667204377661713202948952171655143192075943578946573888576484746209261469970149381872389631389369537155026693263975338398261567274837717090694055171425503933824240291370948820767571
c = 84437879482958388121051989985943610317985560730924629180079819055930253313815835352959163593476985818700482462237552702247843204909498317690512763185777267125647066466604295815291929505489611365030554559376546705541333232100362213541469056985011640358767366350305910694542127597286950765375388740496062563517
hint1 = 737132842226563731129
hint2 = 1083219649182192077965分析:
e很大跟n接近,分析一下大概的大小关系
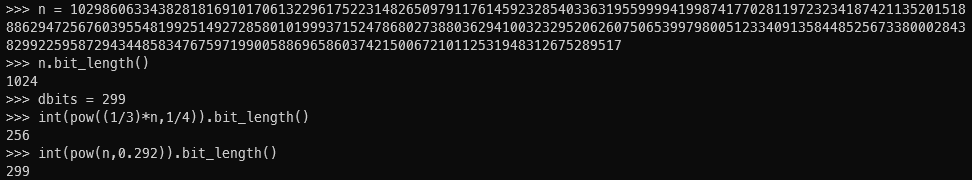
发现 ,应该说刚好卡着上界,是
先看一下常规的Boneh and Durfee attack:
但这题有些不同的是,给了的是p,q的高位,这里稍作修改
套个Boneh and Durfee attack的板子,修改一下就行
原有的脚本里的m=4,这里需要调大些
题解:
from __future__ import print_function
import time
from Crypto.Util.number import *
############################################
# Config
##########################################
"""
Setting debug to true will display more informations
about the lattice, the bounds, the vectors...
"""
debug = True
"""
Setting strict to true will stop the algorithm (and
return (-1, -1)) if we don't have a correct
upperbound on the determinant. Note that this
doesn't necesseraly mean that no solutions
will be found since the theoretical upperbound is
usualy far away from actual results. That is why
you should probably use `strict = False`
"""
strict = False
"""
This is experimental, but has provided remarkable results
so far. It tries to reduce the lattice as much as it can
while keeping its efficiency. I see no reason not to use
this option, but if things don't work, you should try
disabling it
"""
helpful_only = True
dimension_min = 7 # stop removing if lattice reaches that dimension
############################################
# Functions
##########################################
# display stats on helpful vectors
def helpful_vectors(BB, modulus):
nothelpful = 0
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
if BB[ii,ii] >= modulus:
nothelpful += 1
print(nothelpful, "/", BB.dimensions()[0], " vectors are not helpful")
# display matrix picture with 0 and X
def matrix_overview(BB, bound):
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
a = ('%02d ' % ii)
for jj in range(BB.dimensions()[1]):
a += '0' if BB[ii,jj] == 0 else 'X'
if BB.dimensions()[0] < 60:
a += ' '
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
a += '~'
print(a)
# tries to remove unhelpful vectors
# we start at current = n-1 (last vector)
def remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, current):
# end of our recursive function
if current == -1 or BB.dimensions()[0] <= dimension_min:
return BB
# we start by checking from the end
for ii in range(current, -1, -1):
# if it is unhelpful:
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
affected_vectors = 0
affected_vector_index = 0
# let's check if it affects other vectors
for jj in range(ii + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# if another vector is affected:
# we increase the count
if BB[jj, ii] != 0:
affected_vectors += 1
affected_vector_index = jj
# level:0
# if no other vectors end up affected
# we remove it
if affected_vectors == 0:
print("* removing unhelpful vector", ii)
BB = BB.delete_columns([ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([ii])
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii-1)
return BB
# level:1
# if just one was affected we check
# if it is affecting someone else
elif affected_vectors == 1:
affected_deeper = True
for kk in range(affected_vector_index + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# if it is affecting even one vector
# we give up on this one
if BB[kk, affected_vector_index] != 0:
affected_deeper = False
# remove both it if no other vector was affected and
# this helpful vector is not helpful enough
# compared to our unhelpful one
if affected_deeper and abs(bound - BB[affected_vector_index, affected_vector_index]) < abs(bound - BB[ii, ii]):
print("* removing unhelpful vectors", ii, "and", affected_vector_index)
BB = BB.delete_columns([affected_vector_index, ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([affected_vector_index, ii])
monomials.pop(affected_vector_index)
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii-1)
return BB
# nothing happened
return BB
"""
Returns:
* 0,0 if it fails
* -1,-1 if `strict=true`, and determinant doesn't bound
* x0,y0 the solutions of `pol`
"""
def boneh_durfee(pol, modulus, mm, tt, XX, YY):
"""
Boneh and Durfee revisited by Herrmann and May
finds a solution if:
* d < N^delta
* |x| < e^delta
* |y| < e^0.5
whenever delta < 1 - sqrt(2)/2 ~ 0.292
"""
# substitution (Herrman and May)
PR.<u, x, y> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
Q = PR.quotient(x*y + 1 - u) # u = xy + 1
polZ = Q(pol).lift()
UU = XX*YY + 1
# x-shifts
gg = []
for kk in range(mm + 1):
for ii in range(mm - kk + 1):
xshift = x^ii * modulus^(mm - kk) * polZ(u, x, y)^kk
gg.append(xshift)
gg.sort()
# x-shifts list of monomials
monomials = []
for polynomial in gg:
for monomial in polynomial.monomials():
if monomial not in monomials:
monomials.append(monomial)
monomials.sort()
# y-shifts (selected by Herrman and May)
for jj in range(1, tt + 1):
for kk in range(floor(mm/tt) * jj, mm + 1):
yshift = y^jj * polZ(u, x, y)^kk * modulus^(mm - kk)
yshift = Q(yshift).lift()
gg.append(yshift) # substitution
# y-shifts list of monomials
for jj in range(1, tt + 1):
for kk in range(floor(mm/tt) * jj, mm + 1):
monomials.append(u^kk * y^jj)
# construct lattice B
nn = len(monomials)
BB = Matrix(ZZ, nn)
for ii in range(nn):
BB[ii, 0] = gg[ii](0, 0, 0)
for jj in range(1, ii + 1):
if monomials[jj] in gg[ii].monomials():
BB[ii, jj] = gg[ii].monomial_coefficient(monomials[jj]) * monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
# Prototype to reduce the lattice
if helpful_only:
# automatically remove
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, modulus^mm, nn-1)
# reset dimension
nn = BB.dimensions()[0]
if nn == 0:
print("failure")
return 0,0
# check if vectors are helpful
if debug:
helpful_vectors(BB, modulus^mm)
# check if determinant is correctly bounded
det = BB.det()
bound = modulus^(mm*nn)
if det >= bound:
print("We do not have det < bound. Solutions might not be found.")
print("Try with highers m and t.")
if debug:
diff = (log(det) - log(bound)) / log(2)
print("size det(L) - size e^(m*n) = ", floor(diff))
if strict:
return -1, -1
else:
print("det(L) < e^(m*n) (good! If a solution exists < N^delta, it will be found)")
# display the lattice basis
if debug:
matrix_overview(BB, modulus^mm)
# LLL
if debug:
print("optimizing basis of the lattice via LLL, this can take a long time")
BB = BB.LLL()
if debug:
print("LLL is done!")
# transform vector i & j -> polynomials 1 & 2
if debug:
print("looking for independent vectors in the lattice")
found_polynomials = False
for pol1_idx in range(nn - 1):
for pol2_idx in range(pol1_idx + 1, nn):
# for i and j, create the two polynomials
PR.<w,z> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
pol1 = pol2 = 0
for jj in range(nn):
pol1 += monomials[jj](w*z+1,w,z) * BB[pol1_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
pol2 += monomials[jj](w*z+1,w,z) * BB[pol2_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
# resultant
PR.<q> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
rr = pol1.resultant(pol2)
# are these good polynomials?
if rr.is_zero() or rr.monomials() == [1]:
continue
else:
print("found them, using vectors", pol1_idx, "and", pol2_idx)
found_polynomials = True
break
if found_polynomials:
break
if not found_polynomials:
print("no independant vectors could be found. This should very rarely happen...")
return 0, 0
rr = rr(q, q)
# solutions
soly = rr.roots()
if len(soly) == 0:
print("Your prediction (delta) is too small")
return 0, 0
soly = soly[0][0]
ss = pol1(q, soly)
solx = ss.roots()[0][0]
#
return solx, soly
def example():
############################################
# How To Use This Script
##########################################
#
# The problem to solve (edit the following values)
#
# the modulus
N = 102986063343828181691017061322961752231482650979117614592328540336319559999419987417702811972323418742113520151888629472567603955481992514927285801019993715247868027388036294100323295206260750653997980051233409135844852567338000284382992259587294344858347675971990058869658603742150067210112531948312675289517
# the public exponent
e = 94332227188033251470419190704216678578924281824166571884737945076375866824249376355159909654478713223003101525619990336866998705667204377661713202948952171655143192075943578946573888576484746209261469970149381872389631389369537155026693263975338398261567274837717090694055171425503933824240291370948820767571
ph = 737132842226563731129
qh = 1083219649182192077965
ph = ph<<(512-70)
qh = qh<<(512-70)
# the hypothesis on the private exponent (the theoretical maximum is 0.292)
delta = .18 # this means that d < N^delta
#
# Lattice (tweak those values)
#
# you should tweak this (after a first run), (e.g. increment it until a solution is found)
m = 7 # size of the lattice (bigger the better/slower)
# you need to be a lattice master to tweak these
t = int((1-2*delta) * m) # optimization from Herrmann and May
X = 2*floor(N^delta) # this _might_ be too much
Y = floor(2^(512-70)) # correct if p, q are ~ same size
#
# Don't touch anything below
#
# Problem put in equation
P.<x,y> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
A = int((N+1)/2-(ph+qh)/2)
pol = 1 + x * (A + y)
#
# Find the solutions!
#
# Checking bounds
if debug:
print("=== checking values ===")
print("* delta:", delta)
print("* delta < 0.292", delta < 0.292)
print("* size of e:", int(log(e)/log(2)))
print("* size of N:", int(log(N)/log(2)))
print("* m:", m, ", t:", t)
# boneh_durfee
if debug:
print("=== running algorithm ===")
start_time = time.time()
solx, soly = boneh_durfee(pol, e, m, t, X, Y)
# found a solution?
if solx > 0:
print("=== solution found ===")
if False:
print("x:", solx)
print("y:", soly)
d = int(pol(solx, soly) / e)
print("private key found:", d)
c = 84437879482958388121051989985943610317985560730924629180079819055930253313815835352959163593476985818700482462237552702247843204909498317690512763185777267125647066466604295815291929505489611365030554559376546705541333232100362213541469056985011640358767366350305910694542127597286950765375388740496062563517
print(long_to_bytes(pow(c, d, N)))
else:
print("=== no solution was found ===")
if debug:
print(("=== %s seconds ===" % (time.time() - start_time)))
if __name__ == "__main__":
example()crypto2
题面:
# coding: utf-8
#!/usr/bin/env python2
import gmpy2
import random
import binascii
from hashlib import sha256
from sympy import nextprime
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
from FLAG import flag
#flag = 'wdflag{123}'
def victory_encrypt(plaintext, key):
key = key.upper()
key_length = len(key)
plaintext = plaintext.upper()
ciphertext = ''
for i, char in enumerate(plaintext):
if char.isalpha():
shift = ord(key[i % key_length]) - ord('A')
encrypted_char = chr((ord(char) - ord('A') + shift) % 26 + ord('A'))
ciphertext += encrypted_char
else:
ciphertext += char
return ciphertext
victory_key = "WANGDINGCUP"
victory_encrypted_flag = victory_encrypt(flag, victory_key)
p = 0xfffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffefffffc2f
a = 0
b = 7
xG = 0x79be667ef9dcbbac55a06295ce870b07029bfcdb2dce28d959f2815b16f81798
yG = 0x483ada7726a3c4655da4fbfc0e1108a8fd17b448a68554199c47d08ffb10d4b8
G = (xG, yG)
n = 0xfffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffebaaedce6af48a03bbfd25e8cd0364141
h = 1
zero = (0,0)
dA = nextprime(random.randint(0, n))
if dA > n:
print("warning!!")
def addition(t1, t2):
if t1 == zero:
return t2
if t2 == zero:
return t2
(m1, n1) = t1
(m2, n2) = t2
if m1 == m2:
if n1 == 0 or n1 != n2:
return zero
else:
k = (3 * m1 * m1 + a) % p * gmpy2.invert(2 * n1 , p) % p
else:
k = (n2 - n1 + p) % p * gmpy2.invert((m2 - m1 + p) % p, p) % p
m3 = (k * k % p - m1 - m2 + p * 2) % p
n3 = (k * (m1 - m3) % p - n1 + p) % p
return (int(m3),int(n3))
def multiplication(x, k):
ans = zero
t = 1
while(t <= k):
if (k &t )>0:
ans = addition(ans, x)
x = addition(x, x)
t <<= 1
return ans
def getrs(z, k):
(xp, yp) = P
r = xp
s = (z + r * dA % n) % n * gmpy2.invert(k, n) % n
return r,s
z1 = random.randint(0, p)
z2 = random.randint(0, p)
k = random.randint(0, n)
P = multiplication(G, k)
hA = multiplication(G, dA)
r1, s1 = getrs(z1, k)
r2, s2 = getrs(z2, k)
print("r1 = {}".format(r1))
print("r2 = {}".format(r2))
print("s1 = {}".format(s1))
print("s2 = {}".format(s2))
print("z1 = {}".format(z1))
print("z2 = {}".format(z2))
key = sha256(long_to_bytes(dA)).digest()
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC)
iv = cipher.iv
encrypted_flag = cipher.encrypt(pad(victory_encrypted_flag.encode(), AES.block_size))
encrypted_flag_hex = binascii.hexlify(iv + encrypted_flag).decode('utf-8')
print("Encrypted flag (AES in CBC mode, hex):", encrypted_flag_hex)
# output
# r1 = 111817653331957669294460466848850458804857945556928458406600106150268654577388
# r2 = 111817653331957669294460466848850458804857945556928458406600106150268654577388
# s1 = 86614391420642776223990568523561232627667766343605236785504627521619587526774
# s2 = 99777373725561160499828739472284705447694429465579067222876023876942075279416
# z1 = 96525870193778873849147733081234547336150390817999790407096946391065286856874
# z2 = 80138688082399628724400273131729065525373481983222188646486307533062536927379
# ('Encrypted flag (AES in CBC mode, hex):', u'6c201c3c4e8b0a2cdd0eca11e7101d45d7b33147d27ad1b9d57e3d1e20c7b3c2e36b8da3142dfd5abe335a604ce7018878b9f157099211a7bbda56ef5285ec0b')分析:
自定义维吉尼亚 + ECDSA共享k + AES
维吉尼亚的解密:
def victory_decrypt(ciphertext, key):
key = key.upper()
key_length = len(key)
plaintext = ''
for i,char in enumerate(ciphertext):
if char.isalpha():
shift = ord(key[i % key_length]) - ord('A')
decrypted_char = chr((ord(char) - ord('A') - shift) % 26 + ord('A'))
plaintext += decrypted_char
else:
plaintext += char
return plaintextECDSA共享k
k = (z1-z2)*invert(s1-s2,n) % n
dA = (s1*k - z1)*invert(r1,n) % nAES解密
cc = long_to_bytes(int(cc,16))
iv = cc[:16]
c = cc[16:]
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)题解:
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from gmpy2 import *
from hashlib import sha256
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad, unpad
n = 0xfffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffebaaedce6af48a03bbfd25e8cd0364141
xG = 0x79be667ef9dcbbac55a06295ce870b07029bfcdb2dce28d959f2815b16f81798
yG = 0x483ada7726a3c4655da4fbfc0e1108a8fd17b448a68554199c47d08ffb10d4b8
r1 = 111817653331957669294460466848850458804857945556928458406600106150268654577388
r2 = 111817653331957669294460466848850458804857945556928458406600106150268654577388
s1 = 86614391420642776223990568523561232627667766343605236785504627521619587526774
s2 = 99777373725561160499828739472284705447694429465579067222876023876942075279416
z1 = 96525870193778873849147733081234547336150390817999790407096946391065286856874
z2 = 80138688082399628724400273131729065525373481983222188646486307533062536927379
k = (z1-z2)*invert(s1-s2,n) % n
print(k)
k = 41166710682323407984109541250081400981796577119230772899908337474502175902010
dA = (s1*k - z1)*invert(r1,n) % n
key = sha256(long_to_bytes(dA)).digest()
cc = '6c201c3c4e8b0a2cdd0eca11e7101d45d7b33147d27ad1b9d57e3d1e20c7b3c2e36b8da3142dfd5abe335a604ce7018878b9f157099211a7bbda56ef5285ec0b'
cc = long_to_bytes(int(cc,16))
iv = cc[:16]
c = cc[16:]
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)
#print(cipher.decrypt(c))
ciph = 'SDSRDO{58UT00432L8228R9E3G927HDWS8D67G2}'
def victory_decrypt(ciphertext, key):
key = key.upper()
key_length = len(key)
plaintext = ''
for i,char in enumerate(ciphertext):
if char.isalpha():
shift = ord(key[i % key_length]) - ord('A')
decrypted_char = chr((ord(char) - ord('A') - shift) % 26 + ord('A'))
plaintext += decrypted_char
else:
plaintext += char
return plaintext
victory_key = "WANGDINGCUP"
print(victory_decrypt(ciph, victory_key))